导致弱电机房路由器断网的原因及之后
一、背景
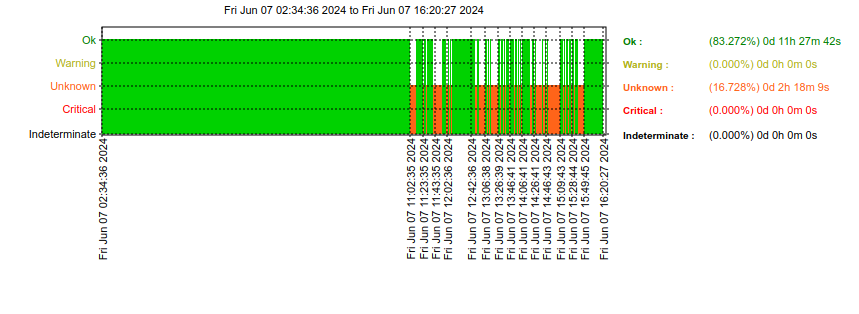
21号夏至这天,刚好请了天假,下午4点左右接到领导电话说是断网了。
想到周四的时候中午11点也出现了断网,通过华三的路由器界面可以看到WAN口显示未连接。到了机房之后,调整了下网线后恢复了。于是,跟领导说弄下网线,但是没有恢复。怀疑是移动的光猫问题,尝试重启后,依然不行。
考虑到马上就要下班了,跟领导说先让大家用手机热点。过了十分钟,想到是否可以重启路由器呢。于是,跟领导说了想法,过了好几分钟,没想到恢复了。
想到路由器的不稳定,是否可以搞一搞呢?替换下路由器?
二、更换设备
说搞就搞。带上panabit ax50c开搞。
配置主要包括出口地址、内网地址、内网DHCP(包括定制DHCP)、默认策略路由、定制策略路由等。
三、处理问题
虽然做了大量努力,还是在周一遇到了些问题。
问题一:域内NAT(回流问题)
之前的H3C路由器支持回流,内网使用公网映射端口进行访问是可以的。但是panabit需要配置一下
floweye nat config nhinstall=1该问题导致财务无法通过公网映射服务访问内部金蝶系统。
问题二:IP地址冲突
刚好有个设备与服务器的ip地址有了冲突,除了补充绑定ip地址与mac地址外,可以在终端测进行
arp -d 192.168.124.92
arp -s 192.168.124.92 76-ea-3c-bc-e0-ad该问题导致容器服务运行失败,以及研发无法连接数据库。
问题三:人力无法访问网站
这个问题比较特殊,但是比较有意思。为了减少机房热量对俺的工控机影响,将其拿到了办公室吹空调。该工控机里面部署了socks代理服务,用于人力使用该服务访问相关网站。由于搬迁过程中服务没有启动所以造成socks无法使用。说起来复杂,本来在总体网络路由层面做了适配,相关网站走内网vpn隧道到通过公网服务器进行访问,但是该机器偏偏开启了代理功能。来回关了三次,每次关闭之后会自动打开。后来搜索了一下,原来人力电脑里有特殊的软件,该软件会读取当前代理pac文件并加入自己的代理,而自己代理用于通过加密隧道访问其服务器。
该问题排查了一大圈才发现原来还有这种操作。
四、事后总结
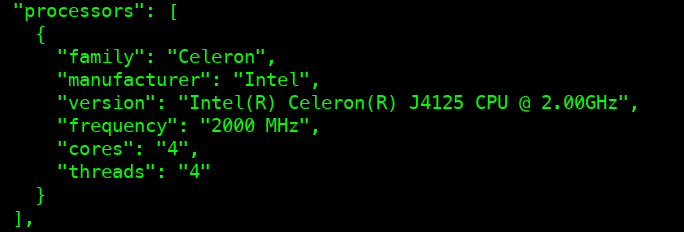
造成断网的原因大概是设备已长时间运行数年之久,且设备大概是十年前的设备,加之机房温度高导致老化加快,运行不稳定。
更换设备过程中,漏了一些没有固定IP地址的DHCP静态配置,给后来的使用带来了一定的困扰。
没有回流设置带来了一些问题,以及服务没有及时启动带来的问题,都给日常的工作增加了不少工作量。